Unit 3 Sections 17-18
Algorithmic Efficiency and Undecidable Problems
- Do Now!!!
Do Now!!!
- Set up your notebook by either wgetting the lesson or tracking it by your own (We would recommend wgetting since there are some fill in the blanks!)
- wget here: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmaxwu/Tri2-GroupFastpages/master/_notebooks/2022-12-dd-lesson.ipynb
3.17: Algorithm Efficiency
Purpose:
The purpose of this lesson is to help students understand how to make an efficient program and optimize it and understand its importance to the CSP curriculum.
What is Algorithmic Efficiency?
- The ability of an algorithm to solve a problem in an efficient way
- An efficient algorithm solves a problem quickly and with a minimum amount of resources, such as time and memory.
- How do we determine if an algorithm is efficient or not?
- One way we can do this is by determining the time complexity of the algorithm.
- Another way is through space complexity.
Traveling Merchant Problem Hacks:
What did you and your team discuss? (record below)
- An heuristic solution is an approach to a problem that produces a solution that isn't necessarily optimal but can be used when normal methods take forever
Describe the method used to solve the traveling merchant problem. (record below)
3.18: Undecidable Problems
Purpose:
The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to the concept of undecidable problems in computer science and to explain why these problems are important.
Key vocabulary:
- Decision problem
- Decidable problem
- Undecidable problem
Decision Problem
A decision problem is a problem in computer science and mathematics that can be solved by a yes-no answer, also known as a binary answer. In other words, a decision problem is a problem for which there are only two possible outputs:"yes" or "no". There are two types of decision problems that Collegeboard goes over:
- Decidable Problems
- Undecidable Problems
A decidable problem is a problem in computer science and mathematics for which an algorithm can be created that can always produce a correct answer or solution. In other words, a decidable problem is a problem for which there exists an algorithm that can be used to determine whether a given input is a valid solution or not.
An undecidable problem is a problem in computer science and mathematics for which it is impossible to create an algorithm that can always provide a correct answer or solution. This means that it is not possible for an algorithm to always determine whether a given input is a valid solution to an undecidable problem.
def divideThirteen(number):
if number % 13 == 0:
return True
else:
return False
print(divideThirteen(26))
print(divideThirteen(30))
An Example of a Forever Running Code
The code keeps adding 1 to the variable number until number is no longer an integer(This is not the python data type "integer", it's the integer in number theory). However, there is no end to this code, making the computer run forever. There is no halt to the code.
i = 0
number = 1
def integerTest(n):
# Testing if the number is an integer
if n%1 ==0:
return True
else:
return False
# Using while loop to keep searching an a non-integer above 1. Note that the computer runs forever.
while i == 0:
number += 1
if integerTest(number) == False:
i +=1
print("Done")
Halting Problem Example:
- In order to understand this, suppose that an algorithm was able to analyze whether a code halts or not. Let's call this algorithm
HaltChecker. -
HaltCheckeranalyzes the program,program P, and its input,input I. Ifprogram Phalts withinput I,HaltCheckerreturns an output of "halts". Ifprogram Pdoesn't halt(runs forever) withinput I,HaltCheckerreturns an output of "never". For example, in the code where it tests if variable number, the code runs forever, soHaltCheckerreturns an output of "never"". - Then, we add another algorithm called
Reverserwhich reversesHaltChecker's output. So, if "never" is the output ofHaltChecker, then the output ofReverseris "hals"". It's also the same the other way around: ifHaltCheckerhas an output of "halts", thenReverserhas an output of "never". - We combine these algorithms into one entire body of code.
- Since
Reverseris the algorithm at the end, hence giving the ultimate output, notice how it prints "never" when in fact there is an end(As proved byHaltChecker), and how it also prints "halts" when there is in fact is no end to the code(Also proved byHaltChecker). As a result,HaltCheckeris inaccurate and this is an undecidable problem.
This Diagram Sums up the Entire Process in the Bulleted List:
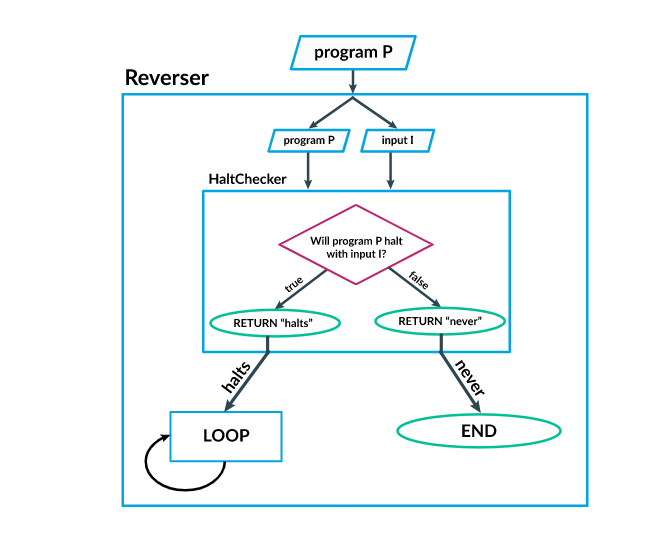
Credits of diagram and example to Khan Academy
FAQ
-
Q: If
Reverseris causing the problem, why not remove it? -
A: Removing
Reverserwill remove the problems, however, we are looking for ways which create the problem of not outputting a correct result. One example is enough to prove that it is an undecidable problem since it proves that the code is not completely accurate.
Extra Things to Notice
- Note that while a computer may take a long time to run a section of code, it does not mean that the computer is going to run forever.
- Humans are able to solve some undecidable problems. The entire Halting Problem example was to prove that computers cannot solve undecidable problems.
Hacks
Come up with one situation in which a computer runs into an undecidable problem. Explain why it is considered an undecidable problem.
One situation in which a computer might run into an undecidable problem is if it is trying to determine whether a given program will run forever or will eventually stop. This is known as the halting problem, and it is considered undecidable because there is no algorithmic way to determine whether a program will halt or not. This is because it is possible for a program to be written in such a way that it can check its own execution and determine whether it will halt or not, but this would require the program to be able to solve the halting problem itself, which is impossible. Therefore, the halting problem is considered undecidable
3.17 Homework
Your homework for Algorithmic Efficiency is pretty simple.
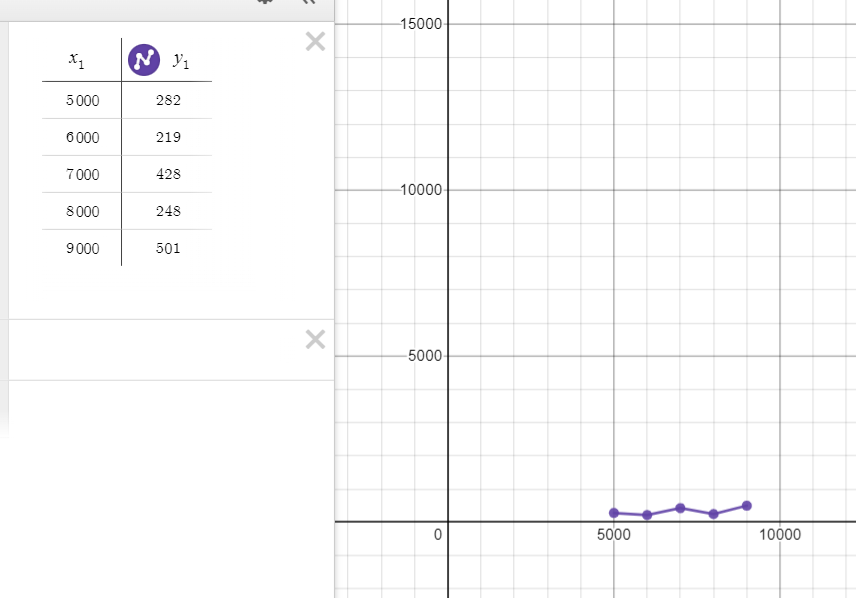
- Use the 1st code below and graph it (Desmos, TI Inpire Cas, e.t.c), change the x value only!
- Label the number of loops done as x and the time (microseconds) to find the index as y
- Connect the points
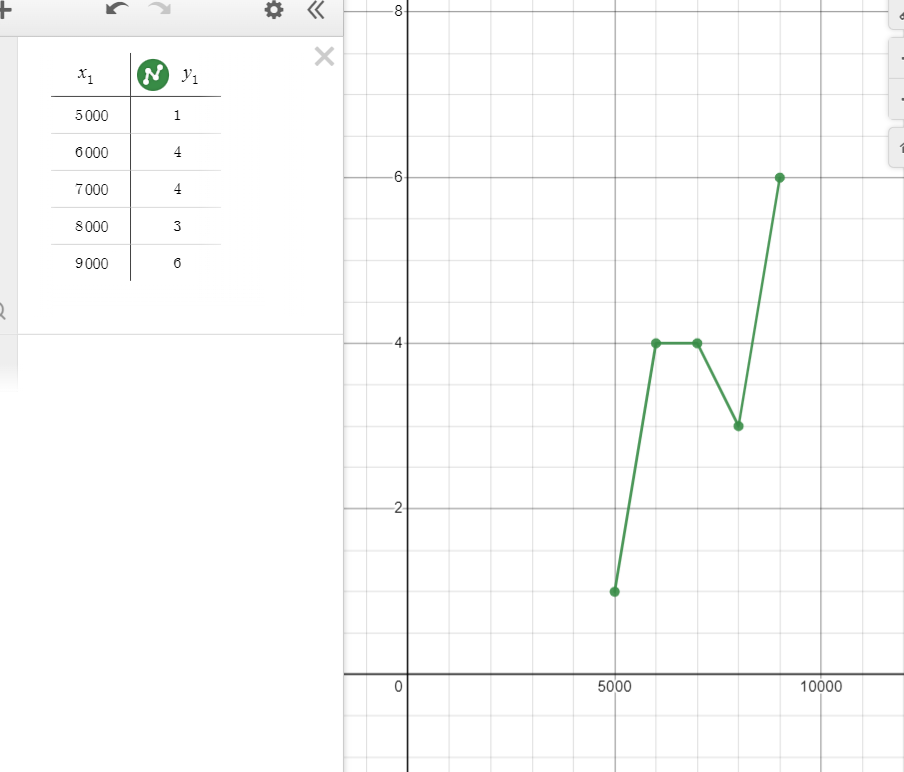
- Do the same thing with the 2nd code
- Compare the two graphs and explain which one of the two is more efficient and why (min. 2 sentences)
- Insert images of the graph either in your blog or on review ticket
The first graph appears to be more linear, whereas the second appears to be a logn graph. The linear graph is always increasing, meaning that the bigger your number is, the longer it takes to identify your number. However, in the second graph, while the curve does increase, it increases slower than the linear one. This means that as the range of a list of numbers increases, the linear graph shows a steeper increase in time than the logn graph. As a result, lists with more numbers will take less time for the logn graph than for the linear graph because the logn graph increases time in very small increments. As a result, the second graph is more efficient. Furthermore, the first graph's points are calculated using linear search, which iterates through each number in the list one by one until the number is identified. The points in the second graph, on the other hand, are calculated using binary search. Binary search divides the list in half each time, and this process is repeated until your number is found. As a result, because binary search is much faster than linear search, the second graph is much more efficient.
import time
def linear_search(lst, x):
start_time = time.perf_counter_ns() # records time (nanoseconds)
for i in range(len(lst)): # loops through the entire list
if lst[i] == x: # until the x value we are looking for is found
end_time = time.perf_counter_ns() # records time again
total_time = (end_time - start_time) // 1000 # subtracts last recorded time and first recorded time
print("Found element after {} loops in {} microseconds".format(i+1, total_time)) # prints the results
return print("Your number was found at", i)
end_time = time.perf_counter_ns() # records the time again
total_time = (end_time - start_time) // 1000 # subtracts last recorded time and first recorded time
print("Element not found after {} loops in {} microseconds".format(len(lst), total_time)) # prints the results
return "Your number wasn't found :("
lst = list(range(1, 10001)) # list with numbers 1-10000
x = 9000 # replace with an integer between 1 and 10000 (I suggest big numbers like 500, 2000, so on)
linear_search(lst, x) # runs procedure
import time
def binary_search(lt, x):
start_time = time.perf_counter_ns() # starts timer
low = 0 # sets the lower side
mid = 0 # sets mid value
high = len(lt) -1 # sets the higher side
num_loops = 0 # number of loops the search undergoes to find the x value
while low<=high: # Loop ran until mid is reached
num_loops += 1 # adds one loop each time process is repeated
mid = (low + high) // 2 # takes the lowest and highest possible numbers and divides by 2 and rounds to closest whole #
if lt[mid] == x:
end_time = time.perf_counter_ns() # records time
total_time = (end_time - start_time) // 1000 # time in microseconds
print("Element found after {} loops in {} microseconds".format(num_loops, total_time)) # prints the results
return mid # returns the index value
elif lt[mid] > x: # if mid was higher than x value, then sets new highest value as mid -1
high = mid -1
elif lt[mid] < x:
low = mid + 1 # if mid was lower than x, sets the new low as mid + 1
end_time = time.perf_counter_ns()
total_time = (end_time - start_time) // 1000
print("Element not found after {} loops in {} microseconds".format(num_loops, total_time)) # prints the results
return "Your number wasn't found :("
lt = list(range(1, 10001)) # list with numbers 1-10000
x = 9000 # replace with an integer between 1 and 10000 (I suggest big numbers like 500, 2000, so on)
binary_search(lt, x) # runs procedure
3.18 Homework:
- Use the Jupyter notebook to write an algorithm that solves a decidable problem. You can use math or whatever else you would like to do.
- Write code to get the computer to run forever. Check this example if you need help, but please come up with your own idea.
Homeworks, hacks, and classwork(filled in blanks) for both 3.17 and 3.18 are due on Thursday at 9:00 pm. -0.1 points for each day late.
def find_max(numbers):
# Set the maximum value to the first number in the list
max_value = numbers[0]
# Loop through the rest of the numbers in the list
for num in numbers[1:]:
# If the current number is greater than the maximum value, update the maximum value
if num > max_value:
max_value = num
# Return the maximum value
return max_value
def is_prime(n):
# Given a positive integer n, determine whether it is prime.
# This function is impossible to implement, because it is undecidable.
# Example usage:
is_prime(2) # This number is prime
is_prime(4) # This number is not prime