Mathematical Expressions and Strings
What is an Algorithm?
An algorithm: a set of instructions that can accomplish a specific task.
An Algorithm Has Three Components
- Sequencing: Algorithms do tasks in the order of specification.

- Selection: Helps choose two different outcomes based off a decision.
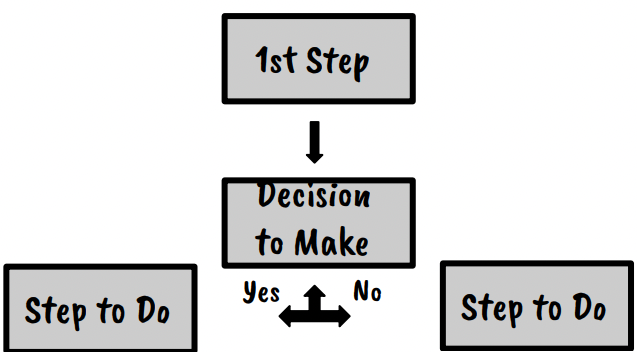
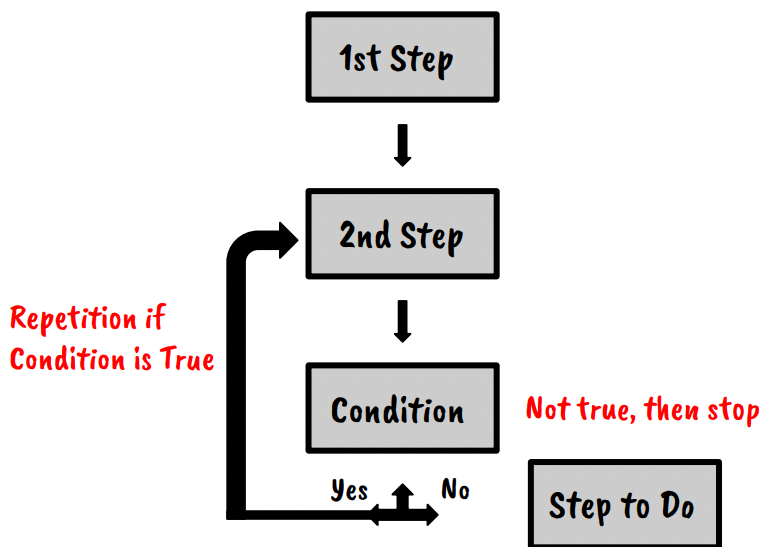
- Iteration: If a condition is true, then the code can repeat.
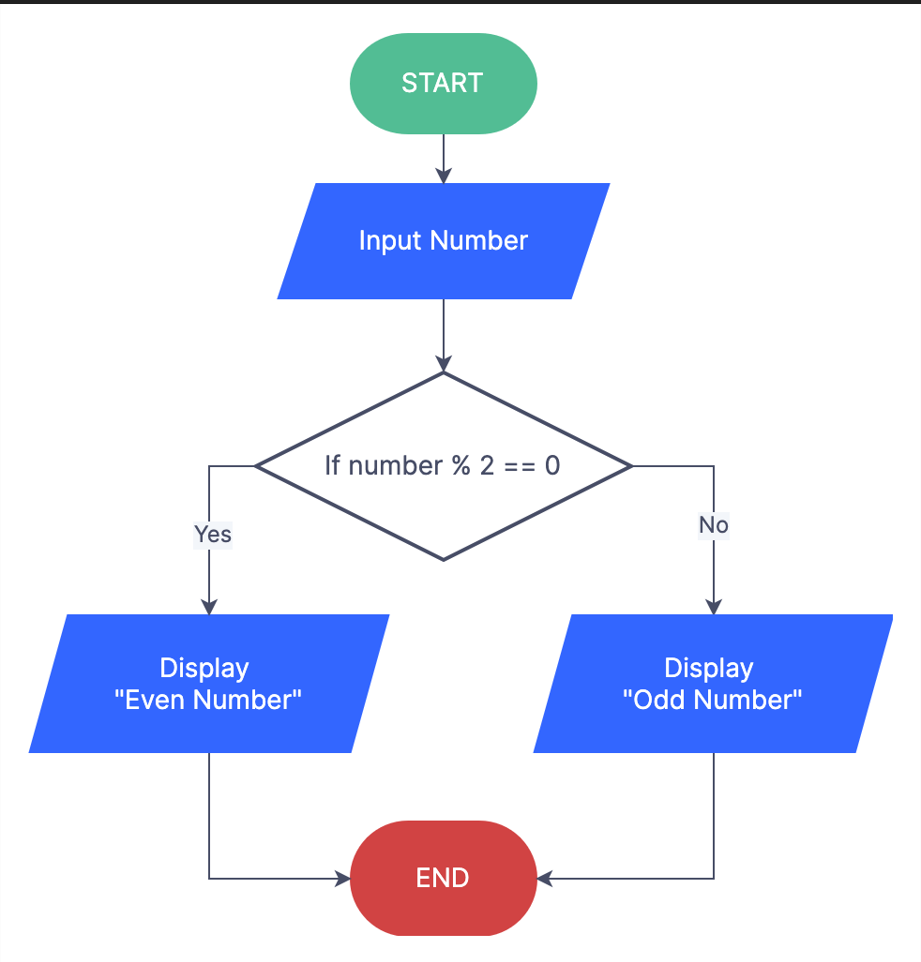
Algorithms Can Be Represented in Two Ways
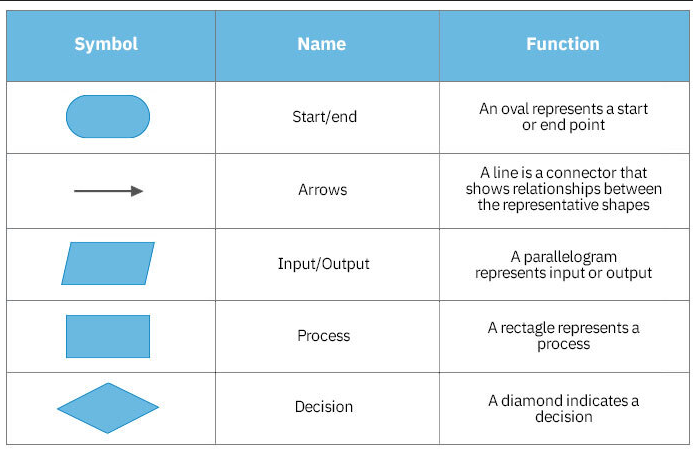
- Flowcharts: Use shapes and arrows to represent the steps of an algorithm.
- Pseudocode: A blend of human language and coding format.
Hacks: Jamboard Flowchart
num1 = 2 - 1
Addition:
- Represented by "+"
num1 = 2 + 1
Multiplication:
- Represented by “*”
num1 = 2 * 1
Division:
- Represented by “/”
num1 = 2 / 1
Getting the Remainder:
- Represented by “MOD” (% in python)
num1 = 5 % 2
print(num1)
num1 = 10
num2 = num1 - 25
num3 = 100 * num1
num4 = num1 / num2
num5 = 9 % num4
Order of Operations
Arithmetic operations in programming are performed in the same order as operations in mathematics:
Operations in parentheses should be done first.
Division and multiplication should be done before addition and subtraction.
Modulus works similar to multiplication and division.
Example: Evaluate num1
num1 = 9 % 2 * ( 8 - 2 ) + 8 / ( 6 - 4 )
print(num1)
score = 0 # 1
score = newScore # 2
score = newScore + 2 # 3
avgScore = allscores(20, 60, 80) # 4
Sequencing is Important!
Changing the order of the steps changes the overall outcome, since every time the value assigned to a variable is changed, it overrides the last value which was assigned to the same variable. That is why it is important to track the value of variables, especially in code where the value is constantly changing.
num1 = 2
num2 = 4
num3 = 6
num1 = num2 + num3 # num1 is now 4 + 6, which is 10
num2 = num1 + num3 # num2 is now (the new num1) 10 + 6, which is 16
# output: num1 = 10, num2 = 16, num3 = 6
VS
num1 = 2
num2 = 4
num3 = 6
num2 = num1 + num3 #num2 is now 8
num1 = num2 + num3 # num1 is now 14
# output: num1 = 14, num2 = 8, num3 = 6
var1 = 9
var2 = 7
var3 = 2
var = var1 + 5
var2 = var1 - var3
var1 = var2
var3 = (var1 + var2) / 2
var2 = 6
print(var1)
print(var2)
print(var3)
Num1 = 50
Num2 = Num1 % 9 + 15
Num3 = Num2 / Num1 + ( Num2 * 2 )
Num4 = Num3 + Num1 / 5 - 10
Result = Num4 - Num2
print(Result)
# it will print 20.4
Num1 = 10
Num2 = Num1 % 3 * 4
Num1 = Num2
Num3 = Num1 * 3
Result = Num3 % 2
print(Result)
# it will print 0
valueA = 4
valueB = 90
valueC = 17
valueB = valueC - valueA
valueA = valueA * 10
if valueB > 10:
print(valueB)
# it will print 13
type = "curly"
color = "brown"
length = "short"
type = "straight"
hair = type + color + length
print(hair)
# it will print straightbrownhair (no spaces)
Strings
What is a String?
A String: A string is a collection of characters. What is a character as character can be anything from numbers, letters, spaces, special symbols, etc.
A string is a collection of characters. What is a character as character can be anything from numbers, letters, spaces, special symbols, etc.
Certain procedures may be used with strings and they vary from programming language to language Python examples
len() to find the length of a string
lower() to convert to lowercase
etc. Pseudocode examples
len() returns the length of a string
concat() returns a string made up of the concatenated strings ex. concat("string1", "string2") would return string1string2
substring() returns the characters from the string beginning at the at the first position to the last so an example of this would be substring ("abcdefghijk", 2, 5) would print bcde (pseudocode starts at 1)
String Concatenation
What is string concatenation?
String concatenation is combining 2 or more strings to make a new strings in order to create a new string
concat() in pseudocode and varys from language to language can be used to combine to strings such as concat("cookie","monster") returns cookiemonster
Substrings
What is a substring?
A substring is a part of and already existing string.
In pseudocode substring() method is used for instance for concat("Mr.Mortenson is very handsome" 1, 2) the system would return Mr (remember that pseudocode starts at 1)
Hacks
Find the result of the following problems. Then convert the pseudocode to working python code using your knowledge of python string operators.
Problem 1
Noun = "Mr.Mortenson"
Adjective = "handsome"
Adjective2 = "Very"
Verb = "is"
abrev = Noun[0:4]
yoda = abrev + " " + Verb + " " + Adjective2 + " " + Adjective
print(yoda)
Noun = "Mr.Mortenson"
Adjective = "handsome"
Adjective2 = "Very"
Verb = "is"
abrev = Noun[:7]
yoda = Adjective2 + " " + Adjective + " " + abrev + " " + Verb + "."
print(yoda)
Problem 2
cookie = "choclate"
cookie2 = "rasin"
len1 = len(cookie) / 2 # 4
len2 = len(cookie2) * 45 #225
vote1 = (cookie, "vote", len2)
vote2 = (cookie2, "vote", len1)
votes = "Chocolate has " + str(len1) + " votes" + " and Rasin has " + str(len2) + " votes"
print(votes)
cookie = "choclate"
cookie2 = "rasin"
len1 = len(cookie) / 2
len2 = len(cookie2) * 45
vote1 = (str(cookie) + " vote " + str(len2))
vote2 = (str(cookie2) + " vote " + str(len1))
votes = (str(vote1) + " " + str(vote2))
print(votes)
Day 2 Topic: Mathematical Expressions and Strings
Algorithms
- a set of instructions that can accomplish a task
- Sequencing= order in which instructions are performed
- Selection= choose which outcome based off a decision
- Iteration= if a condition is true then the code can repeat
Mathematical Expressions
- Arithmetic operations exist in most programming languages
- Subtraction (-), Addition (+), Multiplication (*), Division (/), Remainder(MOD) (%) Order of operations
- parentheses are done first
- then division and multiplication and modulus
- addition and subtraction
Variables
- values can be stored in variables by setting a variable equal to certain values
- sequencing w/ variables takes the most recent assignment
Strings
- collection of characters
- characters can be anything from numbers, letters, spaces, special symbols
- len()= length of a string
- lower()= converts to lowercase
- used to handle textual data